SEO for Beginners: How to Optimize Your Website and Rank Higher on Google
In today’s digital age, having a website is essential for businesses and individuals looking to increase their online visibility. However, simply having a website isn’t enough. To ensure that your site appears in search engine results and attracts traffic, you need to optimize it using SEO (Search Engine Optimization). SEO is the process of enhancing your website to rank higher on Google and other search engines. If you’re new to SEO, don’t worry! This beginner-friendly guide will help you understand the basics and give you actionable steps to improve your website’s ranking.
1. Understanding SEO and Its Importance
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It involves a series of strategies and techniques used to improve your website’s visibility on search engines like Google. When done correctly, SEO can increase organic traffic, which refers to visitors who find your site through search engine results rather than paid ads.
SEO is essential because higher search engine rankings lead to more visibility and, ultimately, more website traffic. Since Google is the most popular search engine globally, focusing on optimizing for Google is the most effective strategy.
Why is SEO important?
- Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more people can find your website.
- More Organic Traffic: The higher your rank, the more likely users are to click on your site.
- Better User Experience: SEO improves site usability, making it easier for visitors to navigate.
- Cost-Effective: Organic traffic is free, unlike paid ads.
2. Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Keyword research is one of the most critical steps in SEO. Keywords are the terms or phrases that people enter into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. By targeting the right keywords, you can ensure that your content aligns with what people are searching for.
How to do Keyword Research:
- Use Keyword Tools: Tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, and Ahrefs can help you identify popular keywords in your niche.
- Focus on Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are more specific and less competitive, making it easier to rank for them (e.g., “best SEO tips for small businesses” instead of just “SEO tips”).
- Analyze Competitors: Check the keywords your competitors are targeting to find gaps in their strategy that you can capitalize on.
Once you have a list of relevant keywords, make sure to integrate them naturally into your website’s content, including headings, titles, meta descriptions, and body text.
3. On-Page SEO: Optimize Your Website’s Content
On-page SEO refers to optimizing individual pages on your website to improve their rankings. Here are some key on-page SEO factors that you should focus on:
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions:
Your title tag is one of the first things Google looks at when indexing a page. It’s also what appears in search results, so it needs to be clear and include your target keyword. Keep it under 60 characters.
Meta descriptions provide a summary of your page’s content and also appear in search results. While meta descriptions don’t directly affect rankings, a compelling description can encourage users to click on your page. Keep it between 150-160 characters.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3):
Use header tags to organize your content and include keywords in these headers. The H1 tag should be used for the main title of the page, and subsequent headers (H2, H3) help structure the content and make it easier to read.
Keyword Optimization:
Don’t stuff your content with keywords; instead, integrate them naturally into your text. Include your target keywords in the first 100 words of the page and spread them throughout the content. Remember to use related keywords and synonyms to help Google understand the context.
Image Optimization:
Images can boost user experience, but they can also slow down your site if they aren’t optimized. Compress images to reduce file size and add descriptive alt text with relevant keywords. This not only improves SEO but also helps with accessibility.
Internal Linking:
Internal links direct users to other pages on your website, helping Google crawl your site more efficiently. It also keeps visitors on your site longer, which can lower your bounce rate. Include relevant internal links to keep your audience engaged.
4. Technical SEO: Enhance Your Website’s Structure
Technical SEO refers to optimizing your website’s backend to ensure that search engines can easily crawl, index, and rank your pages. It also improves your site’s overall performance.
Mobile-Friendly Design:
More than half of internet searches happen on mobile devices. Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. Ensure that your website is responsive and provides a seamless user experience on both desktops and mobile devices.
Site Speed:
Website speed is a crucial ranking factor. Slow loading times can lead to higher bounce rates and a lower user experience. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify ways to improve your site’s speed. Common fixes include image optimization, minifying code, and using a content delivery network (CDN).
Secure Website (HTTPS):
Google prioritizes secure websites, so make sure your site uses HTTPS rather than HTTP. You can get an SSL certificate to make your site secure, ensuring user data is protected.
XML Sitemap and Robots.txt:
Create an XML sitemap to help search engines index your website’s pages more effectively. A robots.txt file guides search engine crawlers on which pages to index or avoid.
5. Off-Page SEO: Build Authority and Trust
Off-page SEO refers to activities outside your website that affect its rankings. The most important off-page SEO factor is backlinks—links from other websites to your pages.
How to Get Backlinks:
- Guest Blogging: Write guest posts on reputable blogs in your industry and include links to your website.
- Content Marketing: Create high-quality, shareable content like infographics, guides, and case studies that naturally attract backlinks.
- Broken Link Building: Find broken links on websites in your niche and offer your content as a replacement.
Social Media Signals:
While social media doesn’t directly impact rankings, having an active social media presence can help increase your website’s visibility and drive traffic.
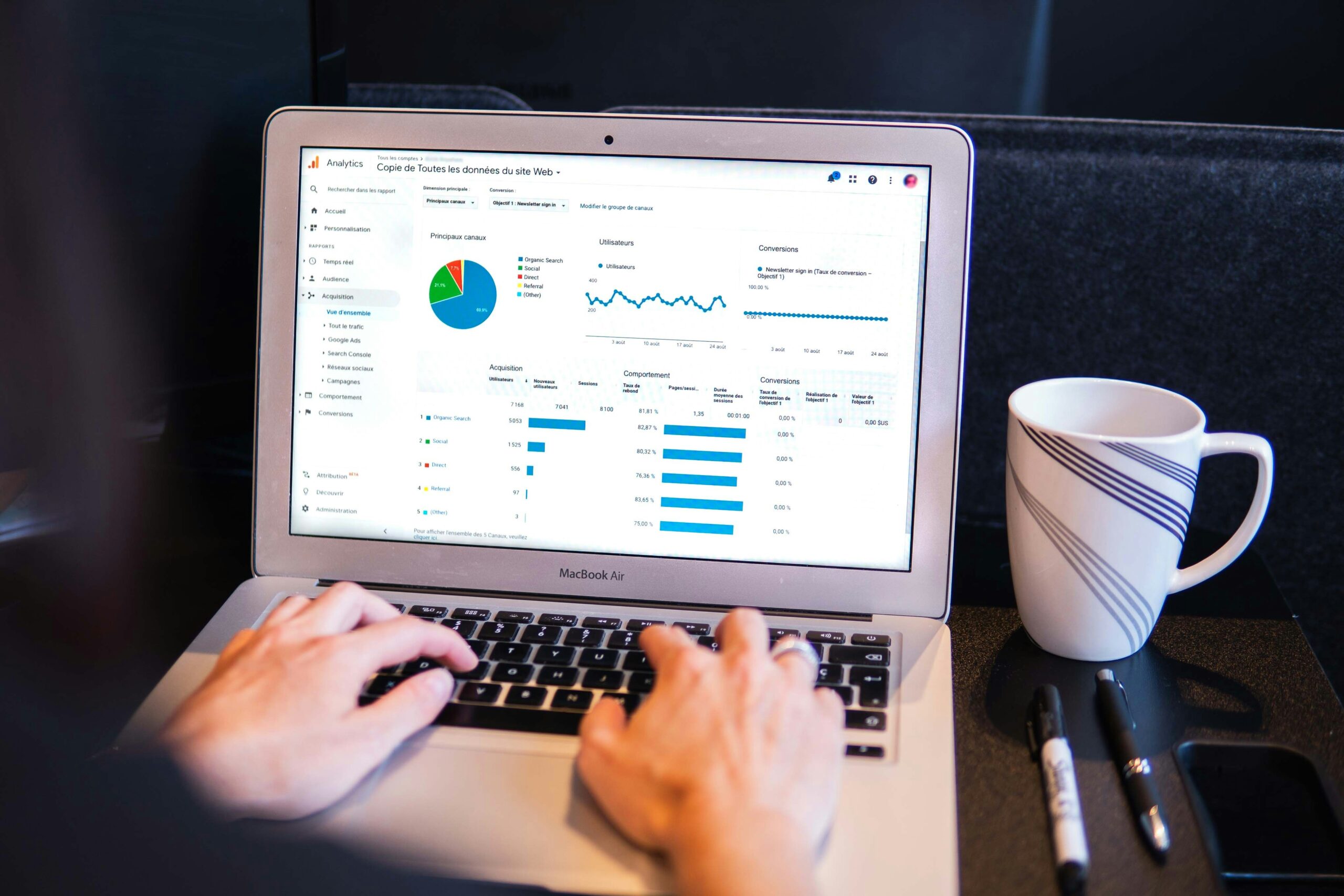
6. Monitor and Analyze Your SEO Performance
SEO is an ongoing process, and it’s important to track your progress. Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor traffic, user behavior, and keyword rankings. These tools provide valuable insights into what’s working and what needs improvement.
Track Key Metrics:
- Organic Traffic: How many visitors are coming from search engines?
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your site without interacting with it.
- Average Time on Page: How long visitors are staying on your pages.
- Conversion Rate: How many visitors take a desired action (e.g., make a purchase or fill out a contact form).
Regularly review your data to adjust your SEO strategy, improve weak areas, and stay competitive.
Conclusion
SEO may seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of the basics and a consistent approach, you can improve your website’s ranking on Google and drive more organic traffic. Focus on keyword research, on-page optimization, technical improvements, and building backlinks to lay the foundation for SEO success. Remember, SEO is a long-term investment, but with patience and dedication, the results will pay off.